Rajnikanth in 3D animation film
Wednesday, January 16, 2008
Thursday, November 15, 2007
Learn ASP.NET
What is ASP.NET?
ASP.NET is a technology for creating dynamic Web applications. It is part of the .NET Framework; you can author ASP.NET applications in most .NET compatible languages, including Visual Basic, C#, and J#. ASP.NET pages (Web Forms) are compiled, providing better performance than with scripting languages. Web Forms allow you to build powerful forms-based Web pages. When building these pages, you can use ASP.NET server controls to create common UI elements, and program them for common tasks. These controls allow you to rapidly build a Web Form out of reusable built-in or custom components, simplifying the code of a page.ASP.NET combines unprecedented developer productivity with performance, reliability, and deployment.
1.Developer Productivity
a.Easy Programming Model.
ASP.NET makes building real world Web applications dramatically easier. ASP.NET server controls enable an HTML-like style of declarative programming that let you build great pages with far less code than with classic ASP. Displaying data, validating user input, and uploading files are all amazingly easy. Best of all, ASP.NET pages work in all browsers -- including Netscape, Opera, AOL, and Internet Explorer.
b.Flexible Language Options
ASP.NET now supports more than 25 .NET languages (including built-in support for VB.NET, C#, and JScript.NET -- no tool required).
c.Great Tool Support.
VS.NET provides integrated support for debugging and deploying ASP.NET Web applications.
d.Rich Class Framework.
The .NET Framework offers over 4500 classes that encapsulate rich functionality like XML, data access, file upload, regular expressions, image generation, performance monitoring and logging, transactions, message queuing, SMTP mail, and much more!
2.Improved Performance and Scalability
a.Compiled execution.
ASP.NET will automatically detect any changes, dynamically compile the files if needed, and store the compiled results to reuse for subsequent requests. Dynamic compilation ensures that your application is always up to date, and compiled execution makes it fast.
b.Rich output caching.
ASP.NET output caching can dramatically improve the performance and scalability of your application. When output caching is enabled on a page, ASP.NET executes the page just once, and saves the result in memory in addition to sending it to the user. When another user requests the same page, ASP.NET serves the cached result from memory without re-executing the page. Output caching is configurable, and can be used to cache individual regions or an entire page. Output caching can dramatically improve the performance of data-driven pages by eliminating the need to query the database on every request.
c.Web-Farm Session State.
ASP.NET session state lets you share session data user-specific state values across all machines in your Web farm. Now a user can hit different servers in the web farm over multiple requests and still have full access to her session. And since business components created with the .NET Framework are free-threaded, you no longer need to worry about thread affinity.
3.Enhanced Reliability
ASP.NET ensures that your application is always available to your users.
Google Android
What is Android?
Android is a software stack for mobile devices that includes an operating system, middleware and key applications. This early look at the Android SDK provides the tools and APIs necessary to begin developing applications on the Android platform using the Java programming language.
Features
- Application framework enabling reuse and replacement of components
- Dalvik virtual machine optimized for mobile devices
- Integrated browser based on the open source WebKit engine
- Optimized graphics powered by a custom 2D graphics library; 3D graphics based on the OpenGL ES 1.0 specification (hardware acceleration optional)
- SQLite for structured data storage
- Media support for common audio, video, and still image formats (MPEG4, H.264, MP3, AAC, AMR, JPG, PNG, GIF)
- GSM Telephony (hardware dependent)
- Bluetooth, EDGE, 3G, and WiFi (hardware dependent)
- Camera, GPS, compass, and accelerometer (hardware dependent)
- Rich development environment including a device emulator, tools for debugging, memory and performance profiling, and a plugin for the Eclipse IDE
Android Architecture
The following diagram shows the major components of the Android operating system. Each section is described in more detail below.
Applications
Android will ship with a set of core applications including an email client, SMS program, calendar, maps, browser, contacts, and others. All applications are written using the Java programming language.
Application Framework
Developers have full access to the same framework APIs used by the core applications. The application architecture is designed to simplify the reuse of components; any application can publish its capabilities and any other application may then make use of those capabilities (subject to security constraints enforced by the framework). This same mechanism allows components to be replaced by the user.
Underlying all applications is a set of services and systems, including:
- A rich and extensible set of Views that can be used to build an application, including lists, grids, text boxes, buttons, and even an embeddable web browser
- Content Providers that enable applications to access data from other applications (such as Contacts), or to share their own data
- A Resource Manager, providing access to non-code resources such as localized strings, graphics, and layout files
- A Notification Manager that enables all applications to display custom alerts in the status bar
- An Activity Manager that manages the lifecycle of applications and provides a common navigation backstack
For more details and a walkthrough of an application, see Writing an Android Application.
Libraries
Android includes a set of C/C++ libraries used by various components of the Android system. These capabilities are exposed to developers through the Android application framework. Some of the core libraries are listed below:
- System C library - a BSD-derived implementation of the standard C system library (libc), tuned for embedded Linux-based devices
- Media Libraries - based on PacketVideo's OpenCORE; the libraries support playback and recording of many popular audio and video formats, as well as static image files, including MPEG4, H.264, MP3, AAC, AMR, JPG, and PNG
- Surface Manager - manages access to the display subsystem and seamlessly composites 2D and 3D graphic layers from multiple applications
- LibWebCore - a modern web browser engine which powers both the Android browser and an embeddable web view
- SGL - the underlying 2D graphics engine
- 3D libraries - an implementation based on OpenGL ES 1.0 APIs; the libraries use either hardware 3D acceleration (where available) or the included, highly optimized 3D software rasterizer
- FreeType - bitmap and vector font rendering
- SQLite - a powerful and lightweight relational database engine available to all applications
Android Runtime
Android includes a set of core libraries that provides most of the functionality available in the core libraries of the Java programming language.
Every Android application runs in its own process, with its own instance of the Dalvik virtual machine. Dalvik has been written so that a device can run multiple VMs efficiently. The Dalvik VM executes files in the Dalvik Executable (.dex) format which is optimized for minimal memory footprint. The VM is register-based, and runs classes compiled by a Java language compiler that have been transformed into the .dex format by the included "dx" tool.
The Dalvik VM relies on the Linux kernel for underlying functionality such as threading and low-level memory management.
Linux Kernel
Android relies on Linux version 2.6 for core system services such as security, memory management, process management, network stack, and driver model. The kernel also acts as an abstraction layer between the hardware and the rest of the software stack.
Wednesday, November 14, 2007
Blackberry Development Using NetBeans Mobility Pack
Requirements
Before you begin, you need to install the following software on your computer:
- NetBeans Integrated Development Environment (IDE) 5.5
- NetBeans Mobility Pack for CLDC/MIDP 5.5
- RIM BlackBerry Java Development Environment (JDE) v4.1
Setting Up for BlackBerry Development
To set up your NetBeans IDE for Blackberry development, you need to add the Blackberry JDE as a custom platform emulator because there are utilities distributed with the JDE that are not distributed with its emulators.
To do this, you perform three steps:
- Add the RIM Blackberry JDE as a custom emulator
- Create a Blackberry project
- Set the Blackberry as the default device emulator
Adding the RIM Blackberry JDE as a Custom Emulator
To begin, you must register the RIM Blackberry emulator using the Java Platform Manager:
- Select Tools > Java Platform Manager from the top navigation bar.
- Click the Add Platform button.
- Select Custom Java Micro Edition Platform Emulator. Click Next.
- The Platform Home should be JDE installation directory (
C:\Program Files\Research In Motion\BlackBerry JDE 4.1.0). - You can enter whatever you want for the Platform Name.
- Set Device Name to one of the supported devices:
7100g, 7100r, 7100t, 7100v, 7100x, 7250, 7290, 7520, - Keep the Preverify Command as it is.
- Modify the Execution and Debugger Commands as shown:
- Execution Command:
cmd /C "cd /D {platformhome}{/}simulator&{device}" - Debugger Command:
cmd /C "cd /D {platformhome}{/}bin&jdwp"
- Execution Command:
- The Bootstrap Libraries panel displays a long list of jar files. Select all of the listed files except
net_rim_api.jarand click Remove. Click Next.
Note: If thenet_rim_api.jaris not in the list, Click the Add button, and type in or navigate toC:\Program Files\Research In Motion\blackberry JDE 4.1.0\lib\net_rim_api.jarand click Open.
Then click Next. - In the Sources and JavaDoc panel, click the Add button next to the JavaDoc window and type in or navigate to:
C:\Program Files\Research In Motion\BlackBerry JDE 4.1.0\docs\api\.The Java Platform Manager should look like the following graphic:
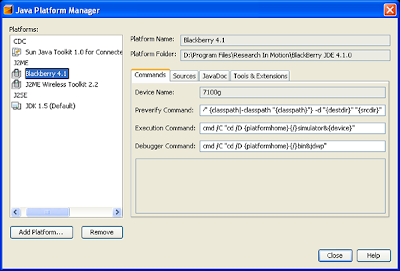
Click Finish, then click Close.
Creating a Blackberry Project
Next, you create a project for your application:
- Choose File > New Project.
- Under Categories, choose Mobile. Under Projects, choose Mobile Application. click Next.
- Give the project a name, for example
MobileApplication2.
If you do not want a sample MIDlet created for your project, uncheck the "Create Hello MIDlet" check box. - Click Finish to create the Project.
- Select the Files Tab in the Explorer window and open the project's
build.xmlfile. Add this (below Image)fragment of code right before the tag at the bottom of the file. 

- If you would like to extend
net.rim.device.api.ui.UiApplicationinstead of standard MIDlets in your project, then:
- Remove the highlighted argument line
build.xmlscript above. - Ignore the warnings in Project Properties / Application Descriptor / MIDlets category when adding a class that does not extend MIDlet.

Set the Blackberry as the Default Device Emulator
Now you're ready to set the default configuration to emulate a Blackberry device:
- Right-click on the project and choose Properties.
- In the Platform Properties:
- Choose Blackberry 4.1 from the Emulator Platform drop-down menu.
- Choose the Blackberry device emulator from the Device drop-down menu.
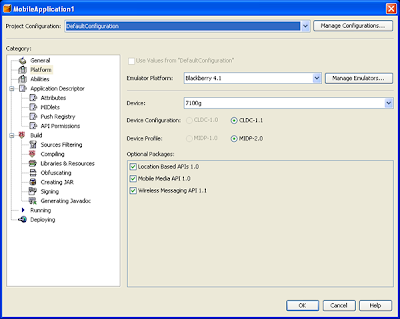
At this point, you are ready to write code, build, run, execute, and debug your MIDlet for the BlackBerry.
Note: Once you build your project and the emulator launches, you will need to scroll to the icon for your application, which will be on the main phone screen when the emulator comes up. You can use the arrow keys or click the scroll wheel on the emulator image to navigate to your application icon.
Saturday, October 27, 2007
Friday, October 26, 2007
Banana

Bananas
Containing three natural sugars - sucrose, fructose and glucose combined with fiber, a banana gives an instant, sustained and substantial boost of energy. Research has proven that just two bananas provide enough energy for a strenuous 90-minute workout. No wonder the banana is the number one fruit with the world's leading athletes. But energy isn't the only way a banana can help us keep fit. It can also help overcome or prevent a substantial number of illnesses and conditions, making it a must to add to our daily diet.
According to a recent survey undertaken by MIND amongst people suffering from depression, many felt much better after eating a banana. This is because bananas contain tryptophan, a type of protein that the body converts into serotonin, known to make you relax, improve your mood and generally make you feel happier.
PMS :
Forget the pills - eat a banana. The vitamin B6 it contains regulates blood glucose levels, which can affect your mood.
Anemia :
High in iron, bananas can stimulate the production of hemoglobin in the blood and so helps in cases of anemia.
Blood Pressure :
This unique tropical fruit is extremely high in potassium yet low in salt, making it the perfect to beat blood pressure.
So much so, the US Food and Drug Administration has just allowed the banana industry to make official claims for the fruit's ability to reduce the risk of blood pressure and stroke
200 students at a Twickenham (Middlesex) school were helped through their exams this year by eating bananas at breakfast, break, and lunch in a bid to boost their brain power. Research has shown that the potassium-packed fruit can assist learning by making pupils more alert.
Constipation :
High in fiber, including bananas in the diet can help
restore normal bowel action, helping to overcome the problem without resorting to laxatives.
Hangovers :
One of the quickest ways of curing a hangover is to make a banana milkshake, sweetened with honey. The banana calms the stomach and, with the help of the honey, builds up depleted blood sugar levels,while the milk soothes and re-hydrates your system.
Heartburn :
Bananas have a natural antacid effect in the body, so if you suffer from heartburn, try eating a banana for soothing relief.
Morning Sickness :
Snacking on bananas between meals helps to keep blood sugar levels up and avoid morning sickness.
Before reaching for the insect bite cream, try rubbing the affected area with the inside of a banana skin. Many people find it amazingly successful at reducing swelling and irritation.
Nerves :
Bananas are high in B vitamins that help calm the nervous system. Overweight and at work? Studies at the Institute of Psychology in Austria found pressure at work leads to gorging on comfort food like chocolate and crisps. Looking at 5,000 hospital patients, researchers found the most obese were more likely to be in high-pressure jobs The report concluded that, to avoid panic-induced food cravings, we need to control our blood sugar levels by snacking on high carbohydrate foods every two
hours to keep levels steady
Ulcers :
The banana is used as the dietary food against intestinal disorders because of its soft texture and smoothness. It is the only raw fruit that can be eaten without distress in over-chronicler cases. It also neutralizes over-acidity and reduces irritation by coating the lining of the stomach.
Temperature control:
Many other cultures see bananas as a "cooling" fruit that can lower both the physical and emotional temperature of expectant mothers. In Thailand , for example, pregnant women eat bananas to ensure their baby is born with a cool temperature.
Seasonal = Affective Disorder (SAD) :
Bananas can help SAD sufferers because they contain the natural mood enhancer tryptophan.
Smoking:
Bananas can also help people trying to give up smoking. The B6,B12 they contain, as well as the potassium and magnesium found in them, help the body recover from the effects of nicotine withdrawal.
Stress :
Potassium is a vital mineral, which helps normalize the heartbeat, sends oxygen to the brain and regulates your body's water balance. When we are stressed, our metabolic rate rises, thereby reducing our potassium levels. These can be balanced with the help of a high-potassium banana snack.
Strokes :
According to research in "The New England Journal of Medicine,"eating bananas as part of a regular diet can cut the risk of death by strokes by as much as 40%!
Warts:
Those keen on natural alternatives swear that if you want to kill off a wart, take a piece of banana skin and place it on the wart, with the yellow side out. Carefully hold the skin in place with a plaster or surgical tape!
So, a banana really is a natural remedy for many ills. When you compare it to an apple, it has four times the protein, twice the carbohydrate, three times the phosphorus, five times the vitamin A and iron, and twice the other vitamins and minerals. It is also rich in potassium and is one of the best value foods around. So maybe its time to change that well-known phrase so that we say, "A banana a day keeps the doctor away!"
Wednesday, October 10, 2007
Java Contact Search for Mobiles
| Features | ||||||||||||||||
|















